Cybercrime-as-a-service Model: How It Works And How It Can Affect You?..
Keep in mind that the primary goal of every cybercriminal is to make as much money as possible. So, the apparition of the cybercrime-as-a-service (CaaS) model was the next inevitable step in pursuing this goal. CaaS, as an organized action, means more revenue with less effort. Hackers are now providing their skills and equipment to anyone ready to pay for it or split the earnings.
CaaS is growing as fast as any thriving business, and it is bad news for every IT specialist, business owner, or even online user. Therefore, its consequences can be as wide as the variety of attacks that are out there. Stealing data, spying on users, and blackmailing, are just a few of them, resulting in empty pockets and destroyed reputations for the victims.
In this article, we will talk about the cybercrime-as-a-service model, how it works, and how can affect you. You will also discover what security measures can protect you from becoming a victim.
What Is Cybercrime-as-a-Service?
Cybercrime-as-a-Service is an organized crime model where threat actors sell their tools, expertise, and services to other people.
Anyone can use CaaS to participate in cybercrime if he is ready to pay for it on the dark web. Hackers no longer need special coding skills, or to develop their own malicious software. They can be the “customers” of a more experienced cybercriminal. The vendor does all the groundwork and sells a ready-to-launch cyberattack.
Cybercrime-as-a-Service can be used to perform a multitude of cybercrimes. Financial Fraud, malware attacks, distributed denial-of-service(DDOS), ransomware, phishing, and social engineering are just some of the possibilities.
How Cybercrime-as-a-Service Works?
A CaaS business has a very clear way of organization, much like a legitimate business. It includes engineers, leaders, and developers to construct the services/tools they are selling. It can even have tech support representatives to help buyers to understand all the technical details of the “product”. And some of the CaaS models offer to host services for launching attacks.
Usually, money mules are also involved. Their goal is to take the earnings to multiple accounts until everybody loses the trace of the money and they become “clean”.
Cybercriminals can rent cyberweapons for their attacks by the hour, day, or month. And the prices can vary a lot: from a few dollars for the simplest kits to hundreds of dollars for the prestigious ones.
For example, you can rent a DDoS booter for $60 a day. But one of the most expensive ransomware kits on the dark web is the Maze Ransomware Kit which can cost $84,000.
If your social media account has been hacked, you can get it back using cybercrime-as-a-service. This service targets Facebook, Instagram, WeChat, TikTok, and Twitter and will cost you $300. Useless to say that, for the same price, you can breach somebody’s else account and get personal.
Sellers can choose to put a price on their merchandise or to get a commission from their affiliates. In the case of ransomware creators, they can agree to receive a certain percentage of the ransom.
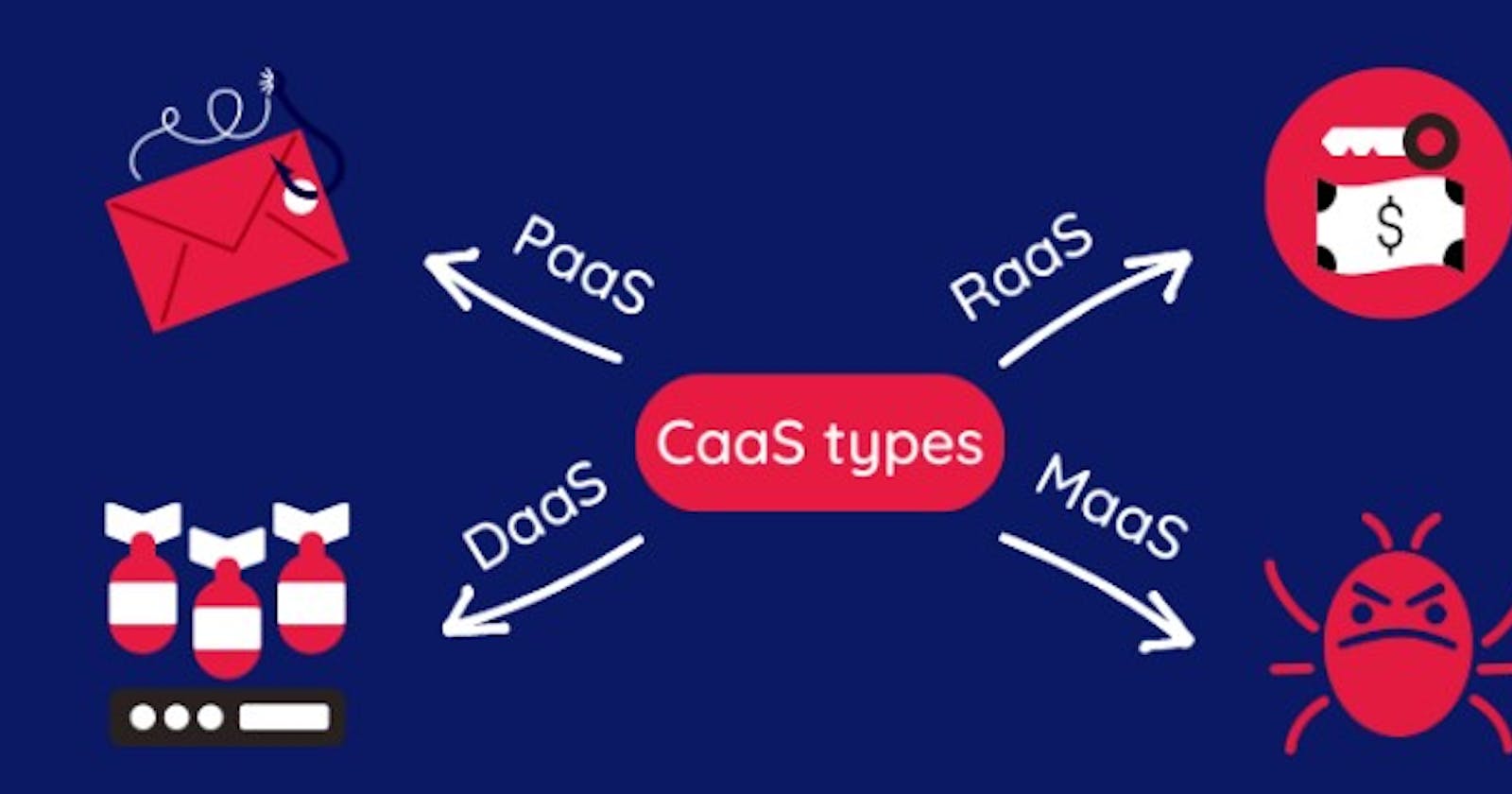
Types of CaaS
Cybercrime-as-a-Service is an umbrella term that includes multiple varieties.
These are the most common types of CaaS:
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
In this case, a cybercriminal creates a malicious code that encrypts a victim’s data and sells it to other individuals who want to carry out ransomware attacks.
RaaS is very popular because it requires little tech skills and basic equipment to deploy it. In addition to that, it provides fast revenue for the hacker using it.
DDoS-as-a-Service
DDOS-as-a-Service offers a hacker access to a botnet – a network of infected devices – so he can carry out a DDoS attack.
In a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack a threat actor floods a server with requests, making it inoperable. This makes the business using this server lose money and reputation, especially if the attack happens at a busy hour.
This service can be used by companies that want to knock down the competition illegally, for example.
Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS)
PhaaS offers a phishing kit for a certain price. This kit contains the tool and knowledge to carry out a phishing attack. Cybercriminals have access to already-made phishing pages, phishing messages, a list of potential victims, etc.
Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS)
Cybercriminals sell malware kits that can be used for spreading viruses and planning trojan attacks, among others.
MaaS owners provide access to a platform for a membership fee. Customers then launch their malicious campaigns using the platform.
Why Is CaaS Dangerous for You?
The presence of CaaS in the cybercrime field has been growing these past few years and there are no signs of slowing down. It becomes more mature and organized.
This upper trend translates into a bigger number of attacks and bigger losses for the victims. Predictions say that in the next 5 years, these losses will keep on growing by 23% per year, reaching a total of $23.84 trillion annually by 2027.
A higher number of threat actors that offer cybercrime-as-a-service services also means lower prices for it. As a result, CaaS is even more appealing and affordable on the black market. Even experienced cybercriminals use it because it allows them to diversify their attacks without much effort.
Taking all these into consideration, we can tell that products and selling offers will only continue to develop in the predictable future. These days, all you need for a cyberattack is money and evil intentions.
How to Stay Protected
You know that the threat of CaaS is out there, so the best thing you can do is to keep informed and take security measures that will protect your data and your organization.
It can be a two-step approach: prevention measures (meant to keep the attackers away) and containment measures (post-incident measures).
Prevention measures
Do penetration testing on your apps, network, endpoints, etc. This way you will find potential vulnerabilities in a secure, controlled environment and you will be able to fix them. It is a good method to ramp up your security and eliminate bugs before cybercriminals can exploit them.
Develop your security suite so it will cover all your attack surfaces. Any security gaps can be a potential entry for hackers.
Your security tools should keep up with the latest threats. Don’t forget that the cybercrime field is always changing!
Invest in security training for your employees. This way your team will be able to recognize a cyberattack and avoid it when possible. Keep in mind that 80% of data breaches begin with a staff member making a mistake.
Containment measures
When you detect an attack, rapidity is essential. Having pre-set policies and procedures will help your team to react faster and contain the infection.
Every person in the organization should know what the next steps are after an incident and who is responsible for what.
Do your best to find the root of the attack. Traffic analysis may help you with that.
Notify clients and authorities about the incident.
A business continuity plan helps you keep operations ongoing and restrain reputation damage.
Wrapping Up…
In conclusion, cybercrime is here to stay. And cybercrime-as-a-service is only a newer and better way of doing it.
To be protected, organizations have to be aware of the threats and invest in prevention. Cybersecurity is a primary need for every company that wants to thrive nowadays.
If you liked this article, follow me on LinkedIn, Twitter, Tumblr, and Contena for more cybersecurity news and topics.